Cable sheathing plays a critical role in protecting cables from external damage and ensuring the safe transmission of electricity and data. The manufacturing process of cable sheathing, known as a “cable sheathing line,” involves a series of specialized machines designed to coat the cable in a protective layer. This article explores the key aspects of the cable sheathing line process, including the materials used, the importance of proper sheathing, and future trends in this essential manufacturing area.
By the end of this article, readers will have a deeper understanding of how cable sheathing is produced, why it is crucial in various industries, and what innovations are shaping the future of cable manufacturing.
2. What is Cable Sheathing?
Definition and Purpose
Cable sheathing refers to the protective outer layer that surrounds electrical cables, protecting the inner conductors from physical damage, chemical exposure, and environmental factors such as moisture and heat. This outer layer is essential for maintaining the integrity of the cable and ensuring the safe transmission of electricity or data.
Materials Used in Cable Sheathing
The materials used in cable sheathing vary depending on the intended application and the environment in which the cables will be used. Common materials include:
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): A versatile material that offers flexibility and resistance to chemicals.
- Polyethylene (PE): Known for its excellent insulation properties.
- Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE): Provides higher thermal resistance, making it ideal for high-voltage applications.
- Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): Offers superior abrasion resistance and flexibility.
3. Cable Sheathing Line Process
Step-by-Step Overview
The cable sheathing line process involves several stages:
- Cable Preheating: The cable is preheated to ensure proper adhesion of the sheathing material.
- Extrusion: Sheathing material is heated and extruded around the cable using an extruder machine.
- Cooling: The sheathed cable passes through cooling systems to solidify the outer layer.
- Inspection and Testing: The sheathed cable undergoes quality checks to ensure the sheath is intact and meets required standards.
- Take-up: The finished cable is wound onto reels for storage or transport.
Machines Involved in Cable Sheathing
- Extruders: These machines heat and shape the sheathing material.
- Cooling Systems: Water or air-cooling systems that help solidify the sheathing material.
- Take-up and Pay-off Systems: These handle the cable before and after the sheathing process, ensuring smooth production flow.
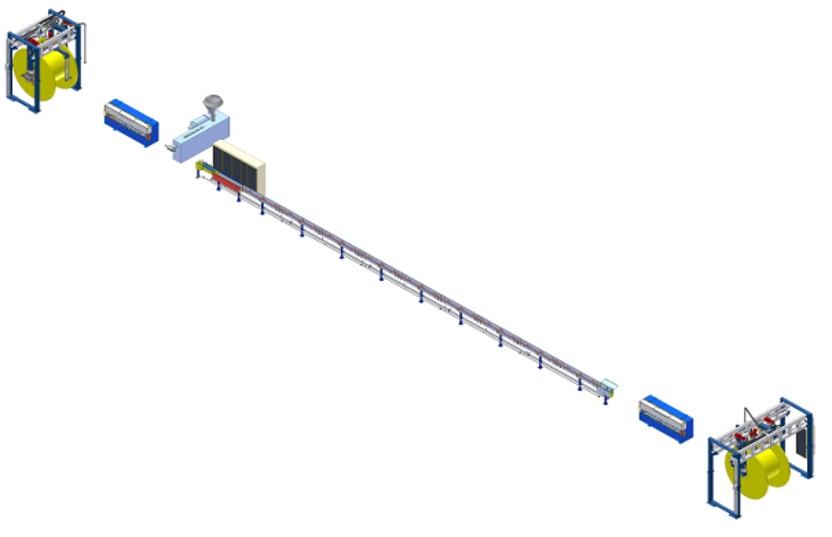
4. Types of Cable Sheathing Materials
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is widely used for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. It also provides good resistance to chemicals and UV exposure, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Polyethylene (PE)
PE is valued for its excellent insulation properties. It offers high resistance to water and is often used in telecommunications cables.
Cross-linked Polyethylene (XLPE)
XLPE is used in high-voltage cables due to its superior thermal resistance. The cross-linking process enhances the material’s strength and heat resistance, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
TPU is known for its abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for cables used in harsh environments such as industrial and automotive settings.
5. Importance of Cable Sheathing in Industry
Protection Against External Elements
Cable sheathing acts as a barrier against moisture, chemicals, and mechanical damage, ensuring the longevity of the cable in harsh environments.
Ensuring Electrical Insulation
Proper cable sheathing ensures that electrical cables do not short circuit or leak electricity, safeguarding equipment and personnel.
Durability and Longevity
By providing a tough exterior, cable sheathing extends the lifespan of cables, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
6. Cable Sheathing Line Equipment
Extruders
Extruders are the heart of the cable sheathing line. They heat and shape the sheathing material, ensuring it forms a uniform coating around the cable.
Cooling Systems
Cooling systems are essential for quickly solidifying the sheathing material, ensuring it adheres properly to the cable without defects.
Take-up and Pay-off Systems
These systems manage the flow of cable through the sheathing line, ensuring smooth production and minimizing waste.
7. Advances in Cable Sheathing Technology
Automation and Robotics
Modern cable sheathing lines are increasingly incorporating automation and robotics to improve efficiency and reduce human error. Automated systems ensure consistent quality and faster production speeds.
Improved Sheathing Materials
New materials are being developed that offer better heat resistance, flexibility, and environmental sustainability. These innovations are helping to meet the demands of industries such as electric vehicles and renewable energy.
8. Key Factors to Consider for Cable Sheathing
Temperature Resistance
In high-temperature environments, choosing a sheathing material that can withstand heat without degrading is crucial for maintaining cable performance.
Flexibility
Cables used in dynamic applications, such as robotics or automotive systems, require flexible sheathing materials that can bend and flex without cracking.
Flame Retardance
In safety-critical applications, flame-retardant sheathing materials are essential to prevent the spread of fire in case of electrical malfunctions.
9. Industry Applications of Cable Sheathing
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, cables must withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. TPU sheathing is often used for its flexibility and abrasion resistance.
Telecommunications
In telecommunications, polyethylene sheathing is preferred for its excellent insulation and resistance to moisture, ensuring reliable signal transmission.
Energy and Power Transmission
High-voltage power cables rely on XLPE sheathing to provide the necessary insulation and heat resistance for safe and efficient power transmission.
10. Case Study: Cable Sheathing in High-Voltage Systems
Challenges
High-voltage systems present unique challenges, including the need for insulation that can withstand extreme temperatures and high electrical loads.
Solutions Implemented
In response to these challenges, XLPE sheathing has become the material of choice for high-voltage cables, offering superior thermal and electrical insulation properties.
11. Future Trends in Cable Sheathing
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Materials
The industry is moving towards more sustainable materials, such as biodegradable sheathing options and recyclable materials, to reduce environmental impact.
Integration with Smart Technologies
Smart cables with built-in sensors are becoming more common. These cables require specialized sheathing that can protect both the conductors and the embedded technology.
12. Practical Tips for Choosing the Right Cable Sheathing Line
Evaluating Needs
Before selecting a cable sheathing line, it’s important to assess the specific needs of your project, such as the environment in which the cables will be used and the expected lifespan.
Assessing Equipment and Material Quality
Investing in high-quality sheathing equipment and materials can prevent costly downtime and ensure the long-term success of your project.
13. Conclusion
Cable sheathing is a critical component in ensuring the safety, durability, and efficiency of electrical systems. From the materials used to the machinery involved in the production process, each aspect plays a vital role in creating cables that can withstand the rigors of their intended applications. As technology continues to evolve, the future of cable sheathing looks bright, with innovations in materials and automation paving the way for more efficient and sustainable production processes.



