Insulation lines are critical in the cable manufacturing industry, ensuring that the insulation covering conductive wires is applied with precision and quality. This article delves into the essential components of insulation lines, from dual-cone payoffs to the electrical control cabinet. The focus will be on the specific equipment mentioned: the dual-cone payoff (630/800 mm), braking unit, extruder, cooling trough, accumulator, automatic double take-up (125/1600 mm), and the electrical control cabinet. These elements work in harmony to produce high-quality insulated cables for various industrial applications.
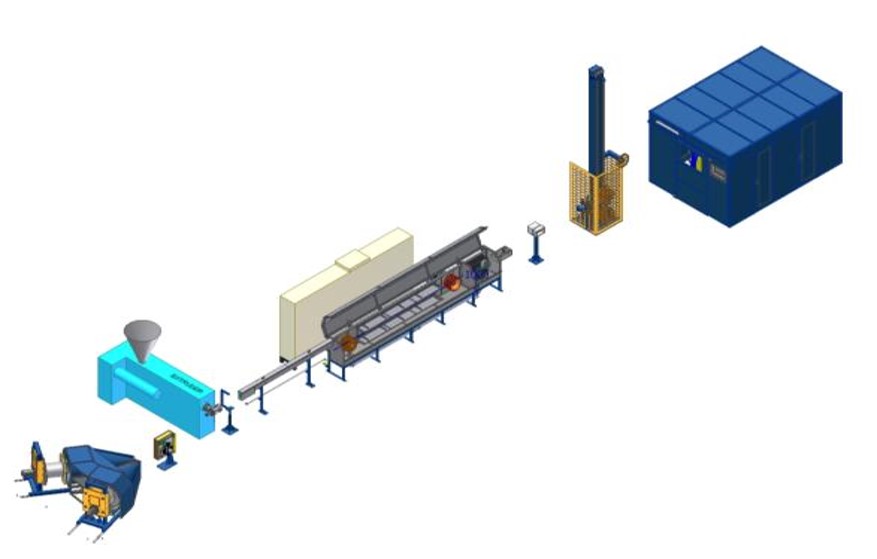
izolasyon hattı – insulation line
What are Insulation Lines?
Insulation lines are production systems designed to apply a protective insulating layer over electrical wires or cables. These lines ensure that conductors are protected from environmental factors such as moisture, extreme temperatures, and electrical interference. The insulation materials typically used include PVC, polyethylene, rubber, or other synthetic compounds, all of which are processed to coat the wires uniformly.
The entire production process is highly automated, requiring specialized machinery that works efficiently to maintain high production rates while ensuring consistent product quality. Now, let’s examine each key piece of equipment within an insulation line and its role.
1. Dual-Cone Payoff 630/800 mm
The dual-cone payoff is the starting point of the insulation line. It is designed to feed wire or cable into the line, ensuring that the process begins with a stable and steady supply of material. The numbers 630 and 800 refer to the diameter of the bobbins (in millimeters) that can be mounted on the payoff, providing versatility depending on the size of the wire or cable being processed.
How It Works
The dual-cone payoff holds a bobbin that contains the conductor wire to be insulated. The machine’s design ensures minimal tension on the wire as it is unspooled, reducing the risk of deformation or stretching. This is crucial for ensuring the final product meets required specifications in terms of diameter and electrical properties.
Dual-cone payoffs are favored for their ability to handle larger bobbins, which means fewer stops for reloading. In high-speed production environments, this efficiency translates to significant cost savings.
Importance of Proper Payoff Setup
Improper setup of the dual-cone payoff can lead to issues such as wire tangling, inconsistent tension, or even production delays. Ensuring that the payoff is appropriately calibrated for the specific wire or cable diameter is crucial for maintaining production efficiency and product quality.
2. Braking Unit
The braking unit is an essential component of the insulation line, responsible for controlling the tension of the wire or cable as it is fed through the system. Without proper tension control, the wire could stretch or compress, which would affect the insulation layer’s uniformity and electrical properties.
Functionality of the Braking Unit
The braking unit works by applying adjustable tension to the conductor as it moves through the line. The unit can be either mechanically or pneumatically controlled, depending on the specific design of the insulation line. In modern systems, braking units are often equipped with sensors that monitor wire tension in real-time, allowing for automatic adjustments to be made when necessary.
Maintaining precise tension control is essential for producing a high-quality insulated cable, as uneven tension can result in weak spots in the insulation layer or affect the conductor’s mechanical properties.
3. Extruder
The extruder is arguably the heart of any insulation line. This machine is responsible for applying the insulation material to the conductor. The process involves heating and melting the insulation material—typically thermoplastics or thermosetting plastics—and then forcing it through a die that shapes the insulation as it is applied to the wire.
The Extrusion Process
The conductor wire passes through the center of the extruder while the melted insulation material is applied around it. The temperature control in the extruder is critical, as the insulation must be heated to the right consistency to flow evenly around the conductor without causing defects such as bubbles or gaps.
Additionally, the extruder must ensure that the insulation layer meets the required thickness and uniformity specifications. This is crucial for the cable’s performance, particularly in applications where electrical resistance and durability are essential.
Key Features of a Modern Extruder
Modern extruders are equipped with advanced control systems that allow for precise adjustment of temperature, pressure, and material flow. This ensures that the insulation is applied consistently, even at high production speeds. Additionally, modern extruders can handle a wide range of insulation materials, offering flexibility in terms of the final product’s properties.
4. Cooling Trough
After the insulation material has been applied to the wire by the extruder, it needs to be cooled and solidified. This is where the cooling trough comes into play. The cooling trough is essentially a long water bath through which the insulated wire passes after extrusion.
Importance of Controlled Cooling
Proper cooling is critical to the insulation process. If the wire cools too quickly or too slowly, it can affect the mechanical properties of the insulation. For instance, rapid cooling can cause the insulation to become brittle, while slow cooling might result in a lack of uniformity or cause the material to shrink unevenly.
In some cases, the cooling trough may include multiple stages or sections with different temperatures, allowing for controlled cooling that ensures optimal material performance.
5. Accumulator
The accumulator is another important element in insulation lines, serving as a buffer between the extruder and the take-up unit. Its primary function is to temporarily store the insulated wire as it exits the cooling trough, ensuring a continuous and uninterrupted production flow.
Role in Maintaining Production Efficiency
Accumulators play a critical role in preventing production stoppages, especially during bobbin changes or other intermittent processes. They help maintain tension and ensure that the wire flows smoothly through the line, even if there are short pauses or adjustments in the take-up section.
6. Automatic Double Take-Up 125/1600 mm
The automatic double take-up system is where the insulated cable is finally collected onto bobbins or spools. The numbers 125 and 1600 refer to the diameter (in millimeters) of the spools that can be used in this system.
Functionality of the Double Take-Up
The double take-up system is designed to automatically switch between two bobbins, allowing for continuous production without stopping the insulation line. This is particularly important in high-volume production settings, where even brief interruptions can lead to significant productivity losses.
Automatic Operation
Modern double take-up units are fully automated, ensuring smooth transitions between spools without manual intervention. This automation reduces downtime and helps maintain high production efficiency. The ability to handle large-diameter spools also means fewer spool changes, further enhancing productivity.
7. Electrical Control Cabinet
The electrical control cabinet is the brain of the insulation line. It houses all the electrical and control components that govern the operation of the various machines within the line. This includes power supplies, motor controls, sensors, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that manage the automation of the system.
Importance of a Centralized Control System
A centralized control system ensures that all components of the insulation line work in harmony. The control cabinet allows operators to monitor and adjust various parameters such as wire tension, extrusion temperature, and take-up speed in real-time. Additionally, it is equipped with safety features to prevent damage to the equipment or injury to operators.
Modern control systems also offer data logging capabilities, allowing manufacturers to track production metrics and ensure that the insulation line operates within the required specifications. This level of control and oversight is essential for producing high-quality insulated cables consistently.
The Synergy of Insulation Line Components
Each piece of equipment in an insulation line plays a crucial role in ensuring the final product meets the required quality standards. From the dual-cone payoff that starts the process, to the electrical control cabinet that manages it all, these machines work in synergy to produce insulated cables that are durable, reliable, and fit for purpose.
Understanding the function of each component—whether it’s maintaining the right tension with the braking unit, applying uniform insulation with the extruder, or ensuring smooth transitions with the automatic double take-up—demonstrates the complexity and precision involved in cable manufacturing. As the demand for high-performance cables continues to grow, the role of advanced insulation lines becomes ever more critical to delivering quality and efficiency in production.
Through proper maintenance, calibration, and operation of these machines, manufacturers can ensure that their insulation lines continue to produce cables that meet the rigorous standards required by industries around the world.



